How it works...
i-MAX & Virtual Reference Station
The Method
Non-standardized methods
Server-controlled network solution
Use of all satellite data NOT maximized
Point of Difference
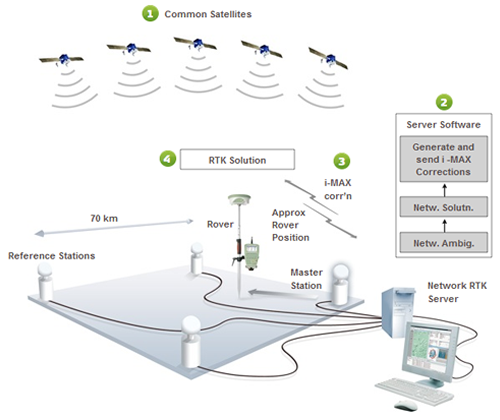
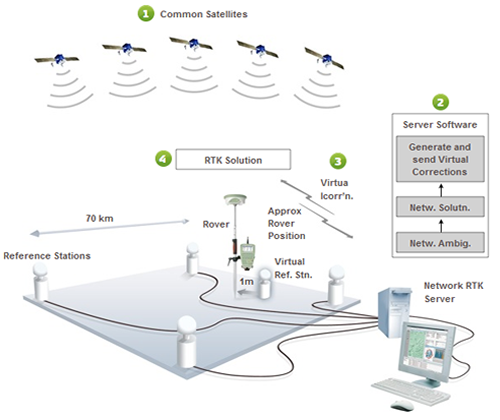
The i-MAX and Virtual Reference Station methods are similar, but not identical. The major point of difference is that the i-MAX method generates corrections for a real reference station instead of a virtual reference station.
Traceability and Repeatability
The i-MAX corrections are related back to a master station. This means that the bas eline between the master station and the measured point can always be directly re-measured. Therefore, the measurements are traceable and repeatable (Fig 3).
With the Virtual Reference Station method the rover does not receive any observations related to a real reference station. This means that the baseline between the virtual reference station and the measured point cannot be directly re-measured. This violates the fundamental surveying principles of traceability and repeatability (Fig 4).
Consistency
The Virtual Reference Station corrections are optimized for the rover position at the beginning of the RTK session (i.e. after connecting to the Network RTK service). If the rover then moves a considerable distance within the same session (i.e. without disconnecting and reconnecting) the corrections might not be appropriate for the new rover location (Landau et al., 2003).
To resolve this issue, the user can disconnect and start a new session to generate a new reference station, or the server may automatically generate a new reference station. However, (in either case) generating new reference stations can cause jumps in position and accuracy. Therefore, the user can end up with inconsistent positions and accuracies throughout their survey.
In contrast, the i-MAX corrections are dynamically updated to follow the movement of the rover. In addition, i-MAX corrections are related back to a real reference station (the master station). This means that the resulting positions and accuracies are consistent.

